What is Random Forest Algorithm?
Byte Size Data Science
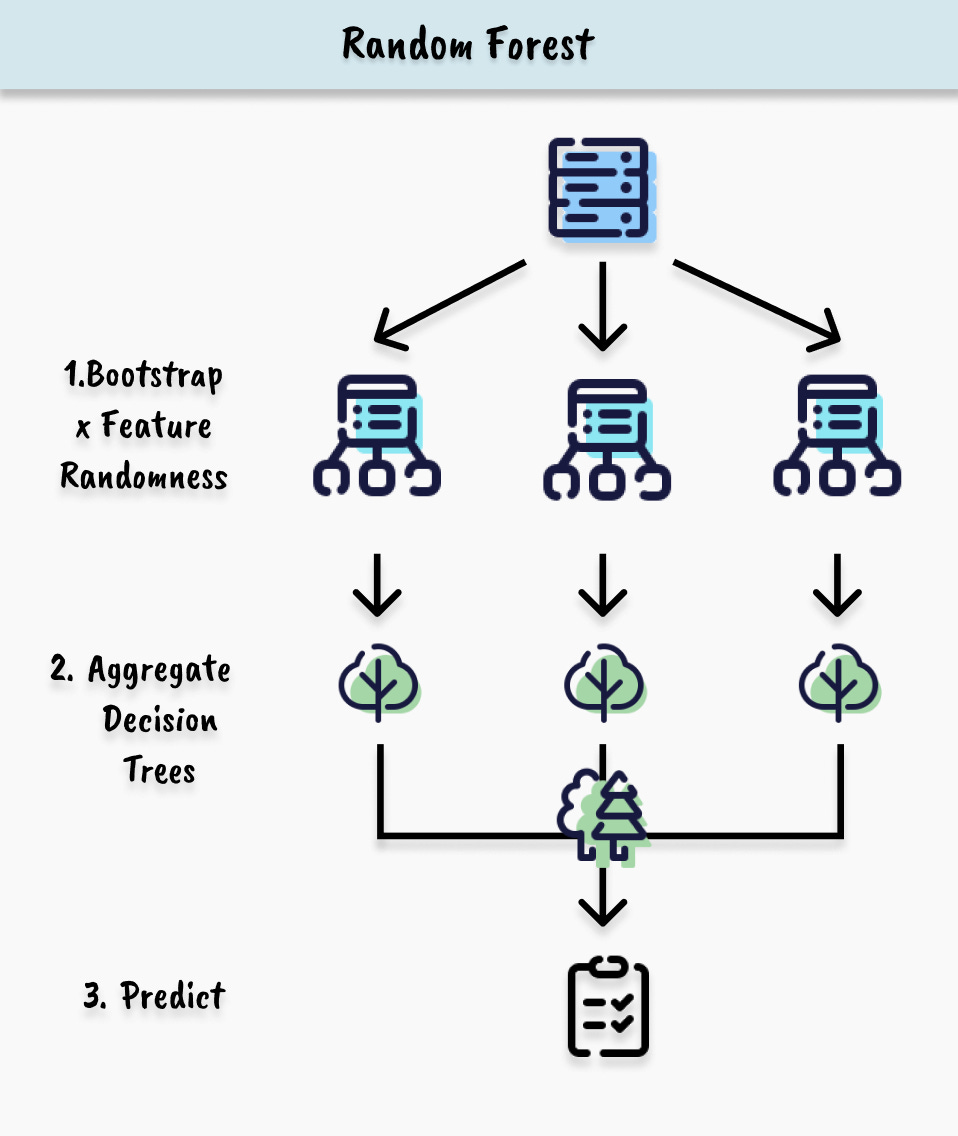
Definition
Random Forest is one of the most popular bagging algorithms that uses decision trees as its base learners. What distinguishes it from other bagging algorithms is its introduction of feature randomness alongside bootstrap sampling. When building each tree, the algorithm not only bootstraps training data but also considers a random subset of features at each split. This allows creating highly diverse trees, each capturing different aspects of the data. Additionally, Random Forest provides powerful capabilities including feature importance measurement, outlier detection, and handling missing data, making it one of the most versatile ensemble methods available.
Implementation
To build a random forest classifier we can import RandomForestClassifier and adjust the model setting using:
n_estimators: the number of decision trees in the random forestoob_score: if out-of-bag samples are used to measure the model accuracymax_depth: set the maximum depth of each decision tree classifier. Limiting max_depth can prevent overfitting.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
rf = RandomForestClassifier(
n_estimators=20,
max_depth=20
oob_score=True
)
rf.fit(X_train,y_train)
y_pred = rf.predict(X_test)Random Forest Classifier produces useful attributes that supports model interpretation, such as feature_importances_ computes the importance of input features and oob_score_ evaluates the model accuracy on out-of-bag samples.